Specific salt effects on thermophoresis of charged colloids
Abstract
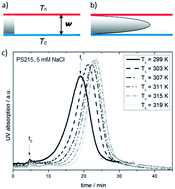
We study the Soret effect of charged polystyrene particles as a function of temperature and electrolyte composition. As a main result we find that the Soret coefficient is determined by charge effects, and that non-ionic contributions are small. In view of the well-known electric-double layer interactions, our thermal field-flow fractionation data lead us to the conclusion that the Soret effect originates to a large extent from diffusiophoresis in the salt gradient and from the electrolyte Seebeck effect, both of which show strong specific-ion effects. Moreover, we find that thermophoresis of polystyrene beads is fundamentally different from proteins and aqueous polymer solutions, which show a strong non-ionic contribution.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...