The heat–chill method for preparation of self-assembled amphiphilic poly(ε-caprolactone)–poly(ethylene glycol) block copolymer based micellar nanoparticles for drug delivery†
Abstract
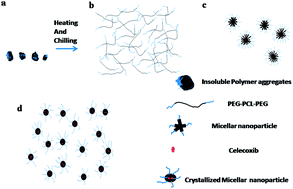
A new method is developed for preparation of amphiphilic block copolymer micellar nanoparticles and investigated as a delivery system for celecoxib, a hydrophobic model drug. Biodegradable block copolymers of poly(ethylene glycol) (PEG) and poly(ε-caprolactone) (PCL) were synthesized by ring opening copolymerization and characterized thoroughly using FTIR, 1H NMR and GPC. The block copolymer was dispersed in distilled water at 60 °C and then it was chilled in an ice bath for the preparation of the micellar nanoparticles. Polymers self-assembled to form micellar nanoparticles (<50 nm) owing to their amphiphilic nature. The prepared micellar nanoparticles were analyzed using HR-TEM, DLS and DSC. The cytotoxicity of the polymer micellar nanoparticles was investigated against HaCaT cell lines. The study of celecoxib release from the micellar nanoparticles was carried out to assess their suitability as a drug delivery vehicle. Addition of the drug to the system at low temperature is an added advantage of this method compared to the other temperature assisted nanoparticle preparation techniques. In a nutshell, polymer micellar nanoparticles prepared using the heat–chill method are believed to be promising for the controlled drug release system of labile drugs, which degrade in toxic organic solvents and at higher temperatures.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...