Nanotribology of biopolymer brushes in aqueous solution using dissipative particle dynamics simulations: an application to PEG covered liposomes in a theta solvent†
Abstract
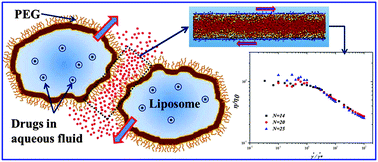
We undertake the investigation of sheared polymer chains grafted onto flat surfaces to model liposomes covered with polyethylene glycol brushes as a case study for the mechanisms of efficient drug delivery in biologically relevant situations, for example, as carriers for topical treatments of illnesses in the human vasculature. For these applications, specific rheological properties are required, such as low viscosity at high shear rates, to improve the transport of the liposomes. Therefore, extensive non-equilibrium, coarse-grained dissipative particle dynamics simulations of polymer brushes of various lengths and shear rates are performed to obtain the average viscosity and the friction coefficient of the system as functions of the shear rate and polymerization degree under theta-solvent conditions, and we find that the brushes experience considerable shear thinning at large shear rates. The viscosity (η) and the friction coefficient (μ) are shown to obey the scaling laws η ∼![[small gamma, Greek, dot above]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/i_char_e0a2.gif) −0.31 and μ ∼
−0.31 and μ ∼ ![[small gamma, Greek, dot above]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/i_char_e0a2.gif) 0.69 at high shear rates (
0.69 at high shear rates (![[small gamma, Greek, dot above]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/i_char_e0a2.gif) ) in a theta solvent, irrespective of the degree of polymerization of brushes. These results confirm recent scaling predictions and reproduce very well trends in measurements of the viscosity at a high shear rate (
) in a theta solvent, irrespective of the degree of polymerization of brushes. These results confirm recent scaling predictions and reproduce very well trends in measurements of the viscosity at a high shear rate (![[small gamma, Greek, dot above]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/i_char_e0a2.gif) ) of red blood cells in a liposome containing medium.
) of red blood cells in a liposome containing medium.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...