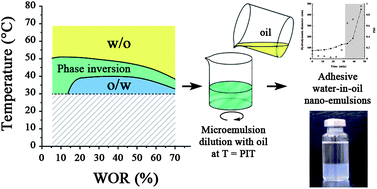
This study aims at exploring and understanding the formulation of reverse (water-in-oil) nano-emulsions by the phase inversion temperature method (PIT method). Over the past decade, low-energy nano-emulsification methods have been largely approached for the formulation of direct (oil-in-water) nano-emulsions. These studies have allowed better understanding in identifying the basic concepts and principles driving the nano-droplet formation processes. In fact, the water-in-oil low-energy nano-emulsification has been much less studied and understood. Recent advances in this field have demonstrated methods and processes based on spontaneous emulsification, however there have been no studies to date describing the driving principles in the production and formulation of reverse nano-emulsions and their link with direct nano-emulsification, especially by the PIT method which still remains challenging. Herein we report for the first time a comprehensive experimental approach that explores and understands the formulation of water-in-oil nano-emulsions by the phase inversion temperature method. The experimental system for emulsion phase inversion was composed of water–paraffin oil–C18E6 (lipophilic polyethoxylated surfactant), which was maintained in the phase inversion zone before its breaking-up by the dilution light oil (2-methylbutane), immediately generating reverse nano-emulsions. The results allowed disclosure of emulsification principles and mechanisms, in the same line as the ones acknowledged for oil-in-water nano-emulsification. The study emphasized that, similarly to direct low-energy nano-emulsification with the oil–surfactant ratio, here the water–surfactant ratio has a strong impact on the resulting nano-emulsion droplet size. Finally, these reverse nano-emulsions showed strong adhesive properties, characterized commonly with macro-emulsions but never observed with nano-emulsions, and thus leading to the formation of nano-emulsion-gels.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...