Self-assembled surfactant cyclic peptide nanostructures as stabilizing agents†
Abstract
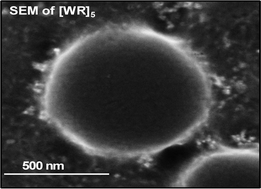
A number of cyclic peptides including [FR]4, [FK]4, [WK]5, [CR]4, [AK]4, and [WR]n (n = 3–5) containing L-amino acids were produced using solid-phase peptide synthesis. We hypothesized that an optimal balance of hydrophobicity and charge could generate self-assembled nanostructures in aqueous solution by intramolecular and/or intermolecular interactions. Among all the designed peptides, [WR]n (n = 3–5) generated self-assembled vesicle-like nanostructures at room temperature as shown by transmission electron microscopy (TEM), scanning electron microscopy (SEM), and/or dynamic light scattering (DLS). This class of peptides represents the first report of surfactant-like cyclic peptides that self-assemble into nanostructures. A plausible mechanistic insight into the self-assembly of [WR]5 was obtained by molecular modeling studies. Modified [WR]5 analogues, such as [WMeR]5, [WR(Me)2]5, [WMeR(Me)2]5, and [WdR]5, exhibited different morphologies to [WR]5 as shown by TEM observations. [WR]5 exhibited a significant stabilizing effect for generated silver nanoparticles and glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase activity. These studies established a new class of surfactant-like cyclic peptides that self-assembled into nanostructures and could have potential applications for the stabilization of silver nanoparticles and protein biomolecules.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...