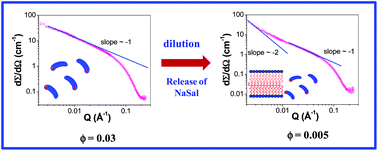
Transformation among various self-assembled structures such as micelles, bilayers, vesicles, etc. is of great relevance in biological systems. Here, we report a dilution-induced structural change from long micelles to bilayers in a cationic–anionic mixture comprising a surfactant, cetyltrimethylammonium bromide (CTAB), and a hydrotrope, sodium salicylate (NaSal). By virtue of the weak hydrophobic nature of hydrotropes, their partitioning between aggregates and bulk solvent is sensitive to the concentration. The dilution induced release of NaSal from CTAB–NaSal mixed micelles, which are rich in hydrotropes (NaSal : CTAB weight ratio 8.5 : 1.5), leads to a transition from long prolate ellipsoidal micelles to bilayers/disks. The structural transition is probed by small angle neutron scattering (SANS), light scattering and rheological studies. SANS studies indicate long prolate ellipsoidal micelles at high concentration, while coexistence of long micelles and bilayers is observed with dilution. The observed structural evolution is explained semi-quantitatively by using a model that takes into account an effective packing parameter for the aggregate.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...