Hydrogels synthesized in electrochemically machined porous Si hosts: effect of nano-scale confinement on polymer properties†
Abstract
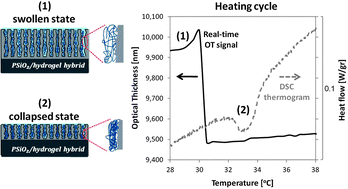
Imprisonment of polymers and hydrogels in inorganic nanostructures is of growing interest in many areas of materials research and various biomedical devices. In this study, we synthesize the hydrogels polyacrylamide and poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) in situ within nanostructured porous Si (PSi) hosts and characterize their thermal properties by differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) and thermal gravimetry. The PSi hosts are electrochemically machined as thin optical Fabry–Pérot films with a well-characterized interconnected nanostructure. Confining hydrogels in these hosts is found to significantly decrease the transition temperatures of the polymers i.e., glass transition temperature (Tg) and temperature-dependent volume phase transition (VPT), in comparison to those of the neat hydrogels. We show that incorporation of a responsive hydrogel, poly(N-isopropylacrylamide), into nanochannels of the PSi thin film permits optical transduction of the hydrogel behavior during its volume phase transition. The “real-time” optical response is correlated with DSC data and provides an alternate means for studying nano-scale confinements of responsive hydrogels. In addition, we found significant differences between the thermal degradation behavior of the confined hydrogels compared with those of neat hydrogels and thin hydrogel films on planar Si surfaces. The confined hydrogels have an inferior thermal stability than that of the neat hydrogels. These findings suggest that the in situ polymerization and the hydrogel confinement conditions have a profound effect on the nanostructure and resulting behavior of the hydrogel phase.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...