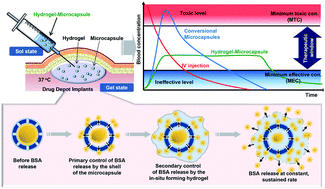
Here, we describe the preparation of microcapsule formulations using in situ-forming hydrogels to achieve desired therapeutic levels over a specific period. Bovine serum albumin (BSA)-fluorescein isothiocyanate (FITC)-loaded microcapsules were prepared using a mono-axial nozzle ultrasonic atomizer with an encapsulation efficiency of approximately 65% and a particle size of approximately 60 μm. Injectable formulations were prepared by mixing BSA-FITC-loaded microcapsules (Cap) and chitosan (CH), Pluronic (PL), or methoxy poly(ethylene glycol)-b-poly(ε-caprolactone) (MPEG-b-PCL) solution (MP). All formulations were prepared as solutions and became gelatinous drug depot implants after injection into the subcutaneous tissue of Sprague-Dawley (SD) rats. While monitoring in vivo BSA release, we found that the initial burst release of BSA was retarded by in situ-forming hydrogels. The Tmax and Cmax values for each formulation were significantly higher and lower, respectively, than those of the BSA-FITC-solution alone. The absolute bioavailability of BSA-FITC from each formulation depended on the viscosities of the in situ-forming hydrogels. The viscosities of the in situ-forming hydrogels were considered to be an important factor influencing the initial burst and duration of BSA release over a period of several weeks. One conclusion that might be drawn from this work is that the initial burst and sustained entire release profile depend on the hydrogel properties. In conclusion, we believe the results of the present study provide potential new insights into sustained pharmacological performance and represent a useful experimental platform using in situ-forming hydrogels for future protein delivery research.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...