Single-phase electrorheological effect in microgravity†
Abstract
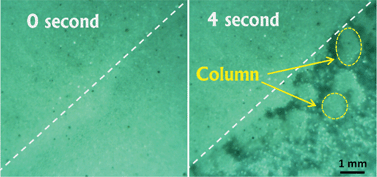
We report the first observation of an electrorheological (ER) effect in a single phase ER suspension, comprising mono-dispersed dielectric particles, from a microgravity experiment. In microgravity, the particles can form stable single phase suspension without a suspending liquid, which is usually necessary for the conventional ER fluid. The size of the column structures formed by the particles exceeds the maximum column width usually observed in the two-phase ER fluids. Numerically evaluating the variation of the electric energy density with respect to the strain yields a good account of the measured data, especially in the low field region.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...