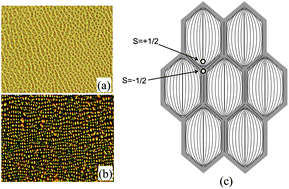
Nematic–nematic phase separation from uniform nematic domain in polymerLC and low-molecular-weight LC mixture showing network lattice formation in pinning stage
Abstract
According to the well-defined phase diagram of a mixture of low-molecular-weight liquid crystal (

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...