In situ remineralizaiton of partially demineralized human dentine mediated by a biomimetic non-collagen peptide
Abstract
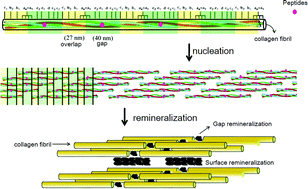
Biomineralization is a well-regulated process mediated by many extracellular
- This article is part of the themed collection: Biomimetic soft matter

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...