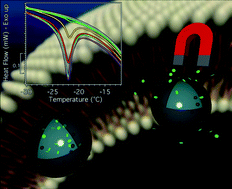
In this paper we describe the effect of a low frequency alternating magnetic field (LF-AMF) on the structure and permeability of magnetoliposomes, i.e. liposomes formulated in the presence of magnetic nanoparticles. Hydrophobic cobalt ferrite nanoparticles (CoFe2O4) coated with a shell of oleic acid were prepared, characterized and employed in the preparation of magnetoliposomes. The stability of the lipid bilayer after the application of an oscillating magnetic field was studied by means of Dynamic Light Scattering (DLS), Small Angle Scattering of X-rays (SAXS) and Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC). The enhancement of liposome permeability upon LF-AMF exposure was measured as the self-quenching decrease of the fluorescent molecule carboxyfluorescein (CF) entrapped in the liposome pool. Carboxyfluorescein leakage from magnetoliposomes was investigated as a function of field frequency, time of exposure to the magnetic field, and cobalt ferrite nanoparticles concentration. Kinetics of CF release from LF-AMF treated magnetoliposomes, monitored through the fluorescence intensity increase during time, highlights a slow release of CF during the first hours, followed by a faster release a few hours after the field treatment which leads to a complete leakage of CF. DSC provides insights about the effect of the LF-AMF treatment, showing that the first few hours correspond to a complete loss of the transition peak from the lamellar gel (Lβ) phase to the liquid crystalline (Lα) phase of the PC bilayers. These results suggest that the slow release takes place through the formation of local pores or defects at the membrane level, while the fast release corresponds to an increased permeability of the membrane that can be related to a structural change of the bilayer.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...