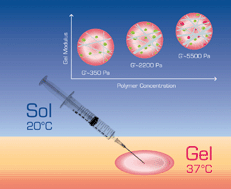
Three dimensional (3D) cell culturing in an artificial matrix needs understanding of the dynamic microenvironments of the extracellular matrix and the cells. In this paper, we investigated a thermal gelling polyalanine–poloxamer–polyalanine (PA–PLX–PA) aqueous solution for chondrocyte 3D culture, focusing on the initial concentration of the polymer aqueous solution. As the polymer concentration increased from 7.0 wt. % to 10.0 wt. % and 15.0 wt. %, moduli of the in situ formed gels at 37 °C were increased from 350–380 Pa to 2100–2300 Pa and 5300–5700 Pa, respectively. In addition, the population and thickness of the nanofibers in the gel were increased. Chondrocytes kept their spherical phenotypes in the 3D environment of the in situ formed PA–PLX–PA hydrogel. They showed excellent cell viability, increased production of sGAG and type II collagen in PA–PLX–PA gel prepared from initial polymer concentration of 7.0 wt. % and 10.0 wt. %, emphasizing the significance of the micromechanical environments for the 3D cell culture.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...