Hierarchical modeling of polymer permeation†
Abstract
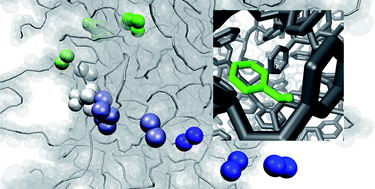
We propose a hierarchical modeling approach for calculating diffusion coefficients and excess chemical potentials of large (non-gaseous) penetrants in
- This article is part of the themed collection: Modelling of Soft Matter

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...