Computer simulation study of the materials properties of intercalated and exfoliated poly(ethylene)glycol clay nanocomposites†
Abstract
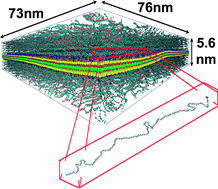
Very large-scale molecular dynamics simulations are performed to investigate the effects of montmorillonite clay filler on poly(ethylene) glycol in the formation of clay-

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...