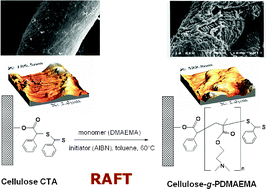
The synthesis and characterization of a novel natural–synthetic hybrid material based on cellulose is reported. The reversible addition–fragmentation chain-transfer (RAFT) process was used to graft poly(2-(dimethylamino)ethyl methacrylate) (PDMAEMA) onto a cellulosic substrate. The weight ratio was increased with an increase in monomer concentration, polymerization time and degree of polymerization (DP). We found that the addition of free chain-transfer agent has a pronounced effect on the weight ratio, chain length of grafted polymer, monomer conversion and homopolymer formation in solution. The cellulose-graft-poly(2-(dimethylamino)ethyl methacrylate) copolymers were characterized by gravimetry, elemental analysis, attenuated total reflectance Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy, scanning electron microscopy, thermal analysis and atomic force microscopy. The dithioester end-group present at the chain end of PDMAEMA was removed viaaminolysis. The livingness of the process was utilized to block-copolymerize styrene from the grafted PDMAEMA chains. The hydrophilic/hydrophobic properties of the novel cellulose-g-(PDMAEMA-b-polystyrene) material were illustrated by contact-angle measurements.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...