A branched nanosheet-interlaced structure of high performance Ni(OH)2 derived from the isostructural Ni3(NO3)2(OH)4 to clarify the role of structure self-supporting in cycling stability†
Abstract
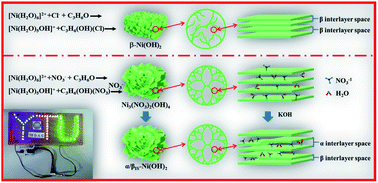
Battery-type electrode materials such as Ni(OH)2 applied in Faraday supercapacitors could present a low cycling stability due to the microstructure damage of materials, originating from their cyclic volume swelling and shrinking. It is well established that the structural stability of materials is crucial for their cycling stability. However, the lack of knowledge about the structural relevance of materials to their cycling stability somehow results in a chaotic understanding on the material design. In this study, we try to reveal the structural relevance by comparing an orderly built nanostructure with a randomly packed nanostructure using Ni(OH)2 as the target material. It is found that the branched nanosheet-interlaced nanostructure of Ni(OH)2 has its self-supportive function in favor of its structural stability, thus promoting its cycling stability. Also, the orderly nanostructured Ni(OH)2 presents high electrochemical performance due to the reduced interfacial charge-transfer resistance and Warburg resistance.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...