Nickel-containing N-doped carbon as effective electrocatalysts for the reduction of CO2 to CO in a continuous-flow electrolyzer†
Abstract
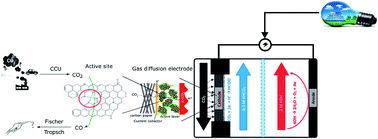
Nickel-containing N-doped carbons were synthesized for the electrochemical reduction of CO2 to CO, which is a promising approach to reduce the atmospheric CO2 levels and its negative impact on the environment. Unfortunately, poor performance (activity, selectivity and/or stability) is still a major hurdle for the economical implementation of this type of materials. The electrocatalysts were prepared through an easily up-scalable and easily tunable method based on the pyrolysis of Ni-containing N-doped carbons. Ni–N–AC–B1 synthesized with a high relative amount of nitrogen and nickel with respect to carbon, was identified as the most promising candidate for this reaction based on its partial CO current density (4.2 mA cm−2), its overpotential (0.57 V) and its faradaic efficiency to CO (>99%). This results in unprecedented values for the current density per g active sites (690 A g−1 active sites). Combined with its decent stability and its high performance in an actual electrolyzer setup, this makes it a promising candidate for the electrochemical reduction of CO2 to CO on a larger scale. Finally, the evaluation of this kind of material in a flow-cell setup has been limited and to the best of our knowledge never included an evaluation of several crucial parameters (e.g. electrolyte type, anode composition and membrane type) and is an essential investigation in the move towards up-scaling and ultimately industrial application of this technique. This study resulted in an optimal cell configuration, consisting of Pt as an anode, Fumatech® as the membrane and 1 M KHCO3 and 2 M KOH as catholyte and anolyte, respectively. In conclusion, this research offers a unique combination of electrocatalyst development and reactor optimization.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...