Metal replacement in perovskite solar cell materials: chemical bonding effects and optoelectronic properties
Abstract
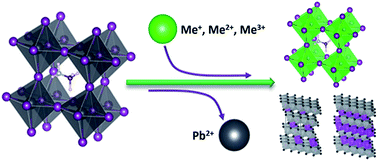
The composition of lead halide perovskite materials has been explored extensively over the last few years and as a consequence, different materials have been introduced into the perovskite solar cell family with diverse physical properties. Herein, we present recent progress within the framework of lead replacement that has led to new solar cell compounds by partial exchange or full substitution of lead with other metals. Lead replacement with divalent metals, tin and germanium perovskites as well as alkaline earth metals, and lanthanides are reviewed and discussed with respect to the chemical bonding effects and their relationship with the optoelectronic and charge mobility properties. The physical properties of the materials and the related device performances are also discussed with respect to the metal cation bonding within the perovskite lattice using transition metals and monovalent and trivalent metals.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...