Mass spectrometric detection of fleeting neutral intermediates generated in electrochemical reactions†
Abstract
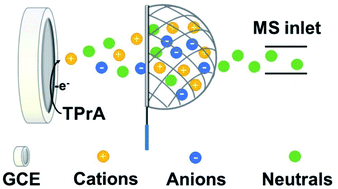
Towards the goal of on-line monitoring of transient neutral intermediates during electrochemical reactions, an electrochemistry-neutral reionization-mass spectrometry (EC-NR-MS) technique was developed in this work. The EC-NR setup consisted of a customized EC flow cell, a sonic spray ionization source, a heating tube, an ion deflector and an electrospray ionization source, which were respectively used for the precise control of the electrochemical reaction, solution nebulization, droplet desolvation, ion deflection and neutral intermediate ionization. Based on the EC-NR-MS approach, some long-sought neutral radicals including TPrA˙, DBAE˙ and TEOA˙, which belong to important reductive intermediates in electrochemiluminescence (ECL) reactions, were successfully identified which helps to clarify the previously unproven ECL reaction mechanism. These findings were also supported by spin-trapping experiments and the tandem MS technique. Accordingly, the EC-NR-MS method provides a direct solution for studying complicated electrochemical reactions, especially for detecting short-lived neutral radicals as well as ionic intermediates.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...