Identification of the peptide epimerase MslH responsible for d-amino acid introduction at the C-terminus of ribosomal peptides†
Abstract
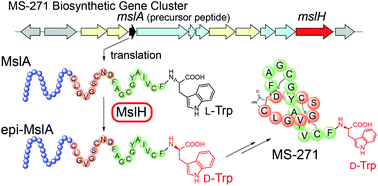
A lasso peptide MS-271 is a ribosomally synthesized and post-translationally modified peptide (RiPP) consisting of 21 amino acids with a D-tryptophan (Trp) at its C terminus. The presence of D-amino acids is rare in RiPPs and few mechanisms of D-amino acid introduction have been characterized. Here, we report the identification of MslH, previously annotated as a hypothetical protein, as a novel epimerase involved in the post-translational epimerization of the C-terminal Trp residue of the precursor peptide MslA. MslH is the first epimerase that catalyzes epimerization at the Cα center adjacent to a carboxylic acid in a cofactor-independent manner. We also demonstrate that MslH exhibits broad substrate specificity toward the N-terminal region of the core peptide, showing that MslH-type epimerases offer opportunities in peptide bioengineering.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...