Amplified detection of nucleic acids and proteins using an isothermal proximity CRISPR Cas12a assay†
Abstract
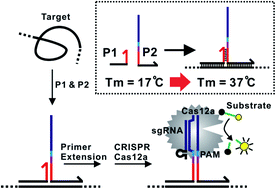
Herein, we describe an isothermal proximity CRISPR Cas12a assay that harnesses the target-induced indiscrimitive single-stranded DNase activity of Cas12a for the quantitative profiling of gene expression at the mRNA level and detection of proteins with high sensitivity and specificity. The target recognition is achieved through proximity binding rather than recognition by CRISPR RNA (crRNA), which allows for flexible assay design. A binding-induced primer extension reaction is used to generate a predesigned CRISPR-targetable sequence as a barcode for further signal amplification. Through this dual amplification protocol, we were able to detect as low as 1 fM target nucleic acid and 100 fM target protein isothermally. The practical applicability of this assay was successfully demonstrated for the temporal profiling of interleukin-6 gene expression during allergen-mediated mast cell activation.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Most popular 2021 chemical biology articles


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...