A rationally designed peptoid for the selective chelation of Zn2+ over Cu2+†
Abstract
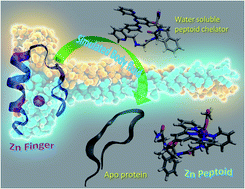
The selective removal of Zn2+ from proteins by using a synthetic chelator is a promising therapeutic approach for the treatment of various diseases including cancer. Although the chelation of Zn2+ is well known, its removal from a protein in the presence of potential competing biologically relevant ions such as Cu2+ is hardly explored. Herein we present a peptoid – N-substituted glycine trimer – incorporating a picolyl group at the N-terminus, a non-coordinating but structurally directing benzyl group at the C-terminus and a 2,2':6′,2′′-terpyridine group in the second position, that selectively binds Zn2+ ions in the presence of excess Cu2+ ions in water. We further demonstrate that this chelator can selectively bind Zn2+ from a pool of excess biologically relevant and competitive ions (Cu2+, Fe3+, Ca2+, Mg2+, Na+, and K+) in a simulated body fluid (SBF), and also its ability to remove Zn2+ from a natural zinc protein domain (PYKCPECGKSFSQKSDLVKHQRTHTG) in a SBF.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...