Nanoscale battery cathode materials induce DNA damage in bacteria†
Abstract
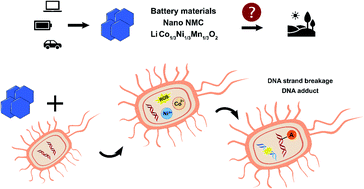
The increasing use of nanoscale lithium nickel manganese cobalt oxide (LixNiyMnzCo1−y−zO2, NMC) as a cathode material in lithium-ion batteries poses risk to the environment. Learning toxicity mechanisms on molecular levels is critical to promote proactive risk assessment of these complex nanomaterials and inform their sustainable development. We focused on DNA damage as a toxicity mechanism and profiled in depth chemical and biological changes linked to DNA damage in two environmentally relevant bacteria upon nano-NMC exposure. DNA damage occurred in both bacteria, characterized by double-strand breakage and increased levels of many putative chemical modifications on bacterial DNA bases related to direct oxidative stress and lipid peroxidation, measured by cutting-edge DNA adductomic techniques. Chemical probes indicated elevated intracellular reactive oxygen species and transition metal ions, in agreement with DNA adductomics and gene expression analysis. By integrating multi-dimensional datasets from chemical and biological measurements, we present rich mechanistic insights on nano-NMC-induced DNA damage in bacteria, providing targets for biomarkers in the risk assessment of reactive materials that may be extrapolated to other nano–bio interactions.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...