Interrogating surface versus intracellular transmembrane receptor populations using cell-impermeable SNAP-tag substrates†
Abstract
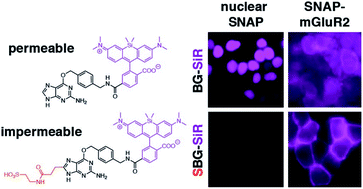
Employing self-labelling protein tags for the attachment of fluorescent dyes has become a routine and powerful technique in optical microscopy to visualize and track fused proteins. However, membrane permeability of the dyes and the associated background signals can interfere with the analysis of extracellular labelling sites. Here we describe a novel approach to improve extracellular labelling by functionalizing the SNAP-tag substrate benzyl guanine (“BG”) with a charged sulfonate (“SBG”). This chemical manipulation can be applied to any SNAP-tag substrate, improves solubility, reduces non-specific staining and renders the bioconjugation handle impermeable while leaving its cargo untouched. We report SBG-conjugated fluorophores across the visible spectrum, which cleanly label SNAP-fused proteins in the plasma membrane of living cells. We demonstrate the utility of SBG-conjugated fluorophores to interrogate class A, B and C G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) using a range of imaging approaches including nanoscopic superresolution imaging, analysis of GPCR trafficking from intra- and extracellular pools, in vivo labelling in mouse brain and analysis of receptor stoichiometry using single molecule pull down.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...