Poly(ethylene glycol) nanocomposites of sub-nanometer metal oxide clusters for dynamic semi-solid proton conductive electrolytes†
Abstract
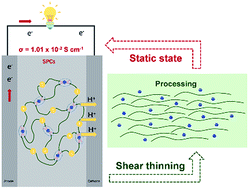
Sub-nm-scale metal oxide clusters (PW12O403−) show high solubility in the melt of poly(ethylene glycol) (PEG) and the obtained semi-solid nanocomposites show promising proton conductivities under ambient conditions. Suggested from scattering studies, the clusters are homogeneously dispersed in the PEG melt at the molecular scale with high loading amounts (70 wt%) and the formed real solutions can be stable for months with no aggregation or phase separation. The conductivities of the nanocomposites which are governed by the concentrations of H3PW12O40 can reach as high as 1.01 × 10−2 S cm−1 at the highest concentration. Due to the dynamic cross-linking hydrogen bonding between clusters and PEG, the nanocomposites behave like solids with negligible flow at high concentrations of clusters. Upon the application of high-speed shear forces (>32 s−1), the composites can flow with continuously decreasing viscosities. The shear thinning properties of the nanocomposites enable their convenient processing into required morphologies and the wettability of electrolytes to electrodes under typical high shear rate processing conditions and the safety of the produced devices can be ensured by their solid-like properties in the static state.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...