A cruciform phthalocyanine pentad-based NIR-II photothermal agent for highly efficient tumor ablation†
Abstract
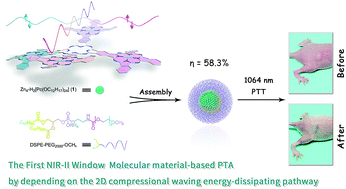
Photothermal therapy in the second near-infrared window (NIR-II, 1000–1700 nm) exhibits a significant advantage over the first near-infrared window (NIR-I, 650–950 nm) in terms of both maximum permissible exposure (MPE) and penetration depth. However, the thus far reported NIR-II photothermal agents (PTAs) have been focused just on inorganic semiconducting and organic polymeric semiconducting nanoparticles. Herein a novel cruciform phthalocyanine pentad was designed, synthesized, and characterized for the first time. The water-soluble nanoparticles (Zn4–H2Pc/DP NPs) assembled from this single molecular material with the help of DSPE–PEG2000–OCH3 exhibit characteristic absorption in the NIR-II region at 1064 nm with a large extinction coefficient of 52 L g−1 cm−1, high photothermal conversion efficiency of 58.3%, and intense photoacoustic signal. Moreover, both in vitro and in vivo studies reveal the good biocompatibility and notable tumor ablation ability of Zn4–H2Pc/DP NPs under 1064 nm laser irradiation. Theoretical density functional theory calculations interpret the two-dimensional compressional wave energy-dissipation pathway over the broad saddle curved framework of the cruciform conjugated phthalocyanine pentad, rationalizing the efficient photothermal properties of corresponding Zn4–H2Pc/DP NPs in the NIR-II window.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...