Boronate affinity-based photoactivatable magnetic nanoparticles for the oriented and irreversible conjugation of Fc-fused lectins and antibodies†
Abstract
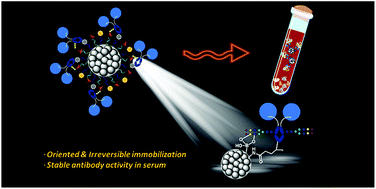
The utilization of immuno-magnetic nanoparticles (MNPs) for the selective capture, enrichment, and separation of specific glycoproteins from complicated biological samples is appealing for the discovery of disease biomarkers. Herein, MNPs were designed and anchored with abundant boronic acid (BA) and photoreactive alkyl diazirine (Diaz) functional groups to obtain permanently tethered Fc-fused Siglec-2 and antiserum amyloid A (SAA) mAb with the assistance of reversible boronate affinity and UV light activation in an orientation-controlled manner. The Siglec-2–Fc-functionalized MNPs showed excellent stability in fetal bovine serum (FBS) and excellent efficiency in the extraction of cell membrane glycoproteins. The anti-SAA mAb-functionalized MNPs maintained active Ab orientation and preserved antigen recognition capability in biological samples. Thus, the BA–Diaz-based strategy holds promise for the immobilization of glycoproteins, such as antibodies, with the original protein binding activity maintained, which can provide better enrichment for the sensitive detection of target proteins.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...