CuxNiy alloy nanoparticles embedded in a nitrogen–carbon network for efficient conversion of carbon dioxide†
Abstract
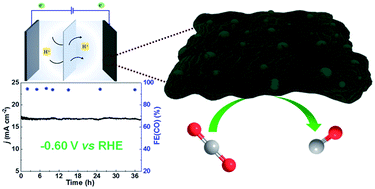
The electrocatalytic conversion of CO2 to CO using non-noble metal catalysts under mild conditions is of great importance. Achieving the combination of high activity, selectivity and current density by developing electrocatalysts with desirable compositions and structures is challenging. Here we prepared for the first time CuxNiy alloy nanoparticles embedded in a nitrogen–carbon network. Such an electrocatalyst not only well overcomes the disadvantages of single Cu and Ni catalysts but has a high CO2 adsorption capacity. Outstandingly, the catalyst can effectively convert CO2 into CO with a maximum faradaic efficiency of 94.5% and current density of 18.8 mA cm−2 at a low applied potential of −0.60 V (versus reversible hydrogen electrode, RHE). Moreover, the catalyst is very stable during long-term electrolysis owing to the stabilization of the nitrogen–carbon network.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...