Design of Pd-based pseudo-binary alloy catalysts for highly active and selective NO reduction†
Abstract
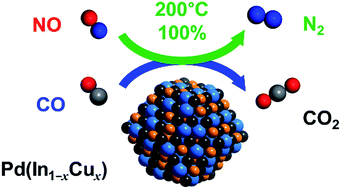
The development of Pd-based alloy catalysts for highly active and selective reduction of NO by CO was investigated. A survey of Pd-based bimetallic catalysts (PdM/Al2O3: M = Cu, In, Pb, Sn, and Zn) revealed that the PdIn/Al2O3 catalyst displayed excellent N2 selectivity even at low temperatures (100% at 200 °C). The catalytic activity of PdIn was further improved by substituting a part of In with Cu, where a Pd(In1−xCux) pseudo-binary alloy structure was formed. The optimized catalyst, namely, Pd(In0.33Cu0.67)/Al2O3, facilitated the complete conversion of NO to N2 (100% yield) even at 200 °C and higher, which has never been achieved using metallic catalysts. The formation of the pseudo-binary alloy structure was confirmed by the combination of HAADF-STEM-EDS, EXAFS, and CO-FT-IR analyses. A detailed mechanistic study based on kinetic analysis, operando XAFS, and DFT calculations revealed the roles of In and Cu in the significant enhancement of catalytic performance: (1) N2O adsorption and decomposition (N2O → N2 + O) were drastically enhanced by In, thus resulting in high N2 selectivity; (2) CO oxidation was promoted by In, thus leading to enhanced low-temperature activity; and (3) Cu substitution improved NO adsorption and dissociation (NO → N + O), thus resulting in the promotion of high-temperature activity.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...