Artificial chimeric exosomes for anti-phagocytosis and targeted cancer therapy†
Abstract
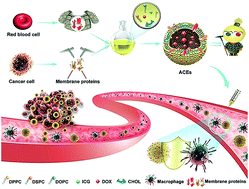
Development of exosome-based delivery systems is still facing some formidable challenges, including the lack of standardized isolation and purification methods, non-large-scale production and low drug-loading efficiency. Inspired by biomimetic technologies, we turned to the design of artificial chimeric exosomes (ACEs) constructed by integrating cell membrane proteins from multiple cell types into synthetic phospholipid bilayers. For benchmarking, hybrid membrane proteins derived from red blood cells (RBCs) and MCF-7 cancer cells were selected as models. The resulting ACEs were engineered much like “Emperor Qin's Terra-Cotta Warriors”, simultaneously equipped with armor (anti-phagocytosis capability from RBCs) and dagger-axes (homologous targeting ability from cancer cells). ACEs demonstrated higher tumor accumulation, lower interception and better antitumor therapeutic effect than plain liposomes in vivo, alongside large-scale standardized preparation, stable structure, high drug-loading capacity and custom-tailored functionality, highlighting the suitability of ACEs as promising alternatives of exosomes in clinical applications.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...