A non-sacrificial method for the quantification of poly(ethylene glycol) grafting density on gold nanoparticles for applications in nanomedicine†
Abstract
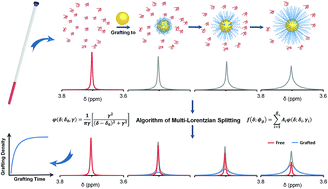
The grafting density of poly(ethylene glycol) (PEG) on nanoparticle (NP) surfaces is the most important parameter determining the interaction of nanoparticles with serum proteins, the subsequent sequestration of the nanoparticle from the bloodstream by the mononuclear phagocyte system, and the eventual delivery efficiency to tumor tissues. However, the majority of in vivo studies do not characterize or report the grafting density of PEG on nanoparticles due to a lack of feasible characterization methods, making it difficult to evaluate the published studies and reconcile apparent conflicting results. Herein, we develop a facile and non-sacrificial 1H NMR analytical approach for the quantitative characterization of grafting density of thiol-terminated PEG (HS-PEG) on gold NPs (GNPs). A multi-Lorentzian-splitting algorithm is used to distinguish the NMR signal of free PEG from those of the grafted ones, therefore allowing in situ monitoring of the grafting process to study the effects of GNP sizes, PEG molecular weights and NP capping ligands on grafting rates and grafting densities. The main advantage of this method is that it is not limited by the types of terminal functional groups on PEG, surface chemistry of the nanoparticles or their composition. It also provides a set of critical and standard guides for characterization of the PEG grafting density on nanoparticles for in vivo biological and biomedical studies.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...