Well-structured bimetallic surface capable of molecular recognition for chemoselective nitroarene hydrogenation†
Abstract
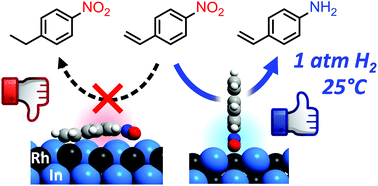
Unprecedented molecular recognition ability governed by a simple bimetallic surface is reported. A series of Rh-based ordered alloys supported on silica gel (RhxMy/SiO2, where M is Bi, Fe, Ga, Ge, In, Ni, Pb, Sb, Sn, or Zn) were tested in the hydrogenation of nitrostyrene to form aminostyrene. RhIn/SiO2 showed remarkably high catalytic activity and good selectivity under 1 atm H2 at room temperature. Moreover, various other nitroarenes containing carbonyl, cyano, or halo moieties were selectively hydrogenated into the corresponding amino derivatives using RhIn/SiO2. Kinetic study and density functional theory (DFT) calculations revealed that the high selectivity originates from RhIn/SiO2 adsorbing nitro groups much more favorably than vinyl groups. In addition, the DFT calculations indicated that the RhIn ordered alloy presents concave Rh rows and convex In rows on its surface, which are able to capture the nitro group with end-on geometry while effectively minimizing vinyl-π adsorption. Thus, the specific and highly ordered surface structure of RhIn enables the chemoselective molecular recognition of nitro groups over vinyl groups through geometric and chemical effects.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...