Insight into the mechanism and outcoupling enhancement of excimer-associated white light generation†
Abstract
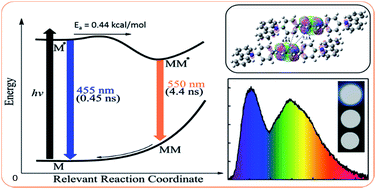
Fundamental insight into excimer formation has been gained by using 9,10-bis[4-(9-carbazolyl)phenyl]anthracene] (Cz9PhAn) as a probe. Cz9PhAn exhibits a highly emissive blue fluorescence in solution and is found to emit a panchromatic white light spectrum (400–750 nm) in film, powder and single crystal, in which an additional excimer band appears at ∼550 nm. Detailed structural analyses, emission relaxation dynamics and a theoretical approach conclude the formation of an anthracene*/phenyl ring excimer through an overlap between π* (anthracene) and π (phenyl ring) orbitals in a face-to-edge stacking orientation. The rate of excimer formation is determined to be 2.2 × 109 s−1 at room temperature, which requires coupling with lattice motion with an activation energy of 0.44 kcal mol−1. Exploiting Cz9PhAn as a single emitter, a fluorescent white organic light emitting diode (WOLED) is fabricated with a maximum external quantum efficiency (ηext) of 3.6% at 1000 cd m−2 (4.2 V) and Commission Internationale de L'Eclairage (CIE) coordinates of (0.30, 0.33). The white-light Cz9PhAn reveals a preferred orientation of the transition dipole moment in the emitting layer to enhance light outcoupling. This non-doped, single component (Cz9PhAn) WOLED greatly reduces the complexity of the fabrication process, rendering a green and cost-effective alternative among the contemporary display/lighting technologies.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...