The functional role of the structure of the dioxo-isobacteriochlorin in the catalytic site of cytochrome cd1 for the reduction of nitrite†
Abstract
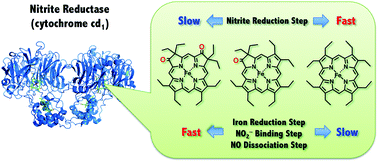
Cytochrome cd1 is a key enzyme in bacterial denitrification and catalyzes one-electron reduction of nitrite (NO2–) to nitric oxide (NO) at the heme d1 center under anaerobic conditions. The heme d1 has a unique dioxo-isobacteriochlorin structure and is present only in cytochrome cd1. To reveal the functional role of the unique heme d1 in the catalytic nitrite reduction, we studied effect of the porphyrin macrocycle on each reaction step of the catalytic cycle of cytochrome cd1 using synthetic model complexes. The complexes investigated are iron complexes of dioxo-octaethylisobacteriochlorin (1), mono-oxo-octaethylchlorin (2) and octaethylporphyrin (3). We show here that the reduction potential for the transition from the ferric state to the ferrous state and the binding constant for binding of NO2– to the ferrous complex increases with a trend of 3 < 2 < 1. However, the reactivity of the ferrous nitrite complex with protons increases in the reversed order, 1 < 2 < 3. We also show that the iron bound NO of the ferric NO complex is readily replaced by addition of 1 equiv. of p-nitrophenolate. These results indicate that the dioxo-isobacteriochlorin structure is superior to porphyrin and mono-oxo-chlorin structures in the first iron reduction step, the second nitrite binding step, and the NO dissociation step, but inferior in the third nitrite reduction step. These results suggest that the heme d1 has evolved as the catalytic site of cytochrome cd1 to catalyze the nitrite reduction at the highest possible redox potential while maintaining its catalytic activity.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...