Unique post-translational oxime formation in the biosynthesis of the azolemycin complex of novel ribosomal peptides from Streptomyces sp. FXJ1.264†
Abstract
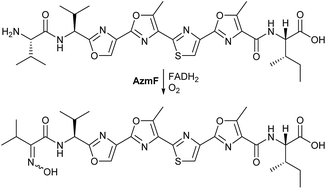
Streptomycetes are a rich source of bioactive specialized metabolites, including several examples of the rapidly growing class of ribosomally-biosynthesized and post-translationally-modified peptide (RiPP) natural products. Here we report the discovery from Streptomyces sp. FXJ1.264 of azolemycins A–D, a complex of novel linear azole-containing peptides incorporating a unique oxime functional group. Bioinformatics analysis of the Streptomyces sp. FXJ1.264 draft genome sequence identified a cluster of genes that was hypothesized to be responsible for elaboration of the azolemycins from a ribosomally-biosynthesized precursor. Inactivation of genes within this cluster abolished azolemycin production, consistent with this hypothesis. Moreover, mutants lacking the azmE and azmF genes accumulated azolemycin derivatives lacking the O-methyl groups and an amino group in place of the N-terminal oxime (as well as proteolysed derivatives), respectively. Thus AzmE, a putative S-adenosyl methionine-dependent methyl transferase, is responsible for late-stage O-methylation reactions in azolemycin biosynthesis and AzmF, a putative flavin-dependent monooxygenase, catalyzes oxidation of the N-terminal amino group in an azolemycin precursor to the corresponding oxime. To the best of our knowledge, oxime formation is a hitherto unknown posttranslational modification in RiPP biosynthesis.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...