Simple electrochemical sensing of attomolar proteins using fabricated complexes with enhanced surface binding avidity†
Abstract
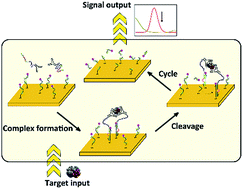
Various strategies have been proposed for the detection of disease protein biomarkers; however, most methods are too expensive, cumbersome or limited in sensitivity for clinical use. Here, we report that a fabricated complex can be used as a powerful tool to detect trace proteins in complex samples. In this strategy, a DNA–protein complex that comprises of one target molecule and two or more deoxyribozyme-containing probes can exhibit autonomous cleavage behavior on the surface of the substrate DNA modified electrode. In the meantime, the complex can remove the cleaved DNA fragment from the electrode surface by taking advantage of the proximity effect. The proposed approach allows one-step and highly sensitive detection of a variety of targets based on the changes of the direct electrochemical readout. Moreover, this method may also have considerable advantages over the commonly reported DNA amplification-assisted immunoassays, particularly in terms of assay simplicity and cost, which may hold great potential for application in resource-constrained regions.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...