Shape and composition control of Bi19S27(Br3−x,Ix) alloyed nanowires: the role of metal ions†
Abstract
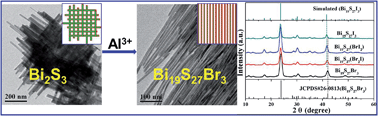
We present the first colloidal synthesis of highly uniform single-crystalline Bi19S27Br3 nanowires (NWs) with a mean diameter of ∼9 nm and tunable lengths in the range of 0.15–2 μm in the presence of foreign metal ions (Al3+). The Al3+ ions not only control the growth of NWs, but also achieve species transformation, i.e., from Bi2S3 to Bi19S27Br3, and are not present in the resulting NWs. This colloidal chemistry approach can be expanded to prepare a family of single-crystalline Bi19S27(Br3−x,Ix) alloyed NWs with controlled compositions (0 ≤ x ≤ 3). Interestingly, these alloyed NWs show an unusual composition-independent band gap of ∼0.82 eV, and theoretical calculations indicate that this phenomenon comes from the very minor contributions of the halogens to the valence band maximum and conduction band minimum. The photodetectors made of Bi19S27(Br3−x,Ix) alloyed NWs show a pronounced photoresponse with high stability and reproducibility, which makes the NWs potentially useful candidates in optoelectronic devices.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...