Utilizing the bioorthogonal base-pairing system of l-DNA to design ideal DNA nanocarriers for enhanced delivery of nucleic acid cargos†
Abstract
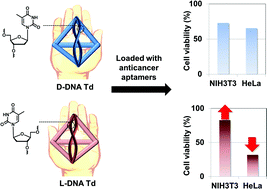
DNA nanoconstructs are a potential drug carrier with high biocompatibility. They are promising particularly when therapeutic nucleic acids are the cargos to be delivered, since both the carrier and the cargo are nucleic acids which can be designed, synthesized and assembled in a seamless feature without using post-synthetic conjugation chemistry. However, the unwanted base-paring events between the cargo and the carrier may potentially disturb the desired structure of the cargo-loaded carrier. To address this concern, we propose a DNA nanocarrier composed of L-DNA strands having a bioorthogonal base-paring system. The study presented here provides useful properties of L-DNA as a backbone for the DNA nanocarrier and demonstrates superiority of L-DNA over the natural D-DNA backbone in the delivery of an anti-proliferative aptamer as well as in the construction of the cargo-carrier assembly.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...