Ultra-fast framework stabilization of Ge-rich zeolites by low-temperature plasma treatment†
Abstract
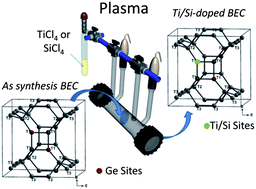
A novel one-step post-synthesis method for structural stabilization of germanium (Ge) silicate molecular sieves is presented. The modification includes low-temperature SiCl4 and TiCl4 plasma treatment of as-synthesized Ge-silicates. During plasma reaction template removal, partial extraction of Ge from the framework and incorporation of Si and Ti in micropore space takes place. The modified material is further subjected to high-temperature calcination, which completes the incorporation of replacing cations in the zeolite framework. The feasibility of this approach for stabilization and modification of Ge-silicate molecular sieves is exemplified by employing Ge-rich BEC-type zeolite as model material. In situ IR spectroscopy is used to monitor the interactions of SiCl4 and TiCl4 precursors with zeolite material and to follow the structural changes provoked by Ge substitution. Ultimate products and their intermediates were subjected to comprehensive characterization employing complementary methods (XRD, SEM/TEM, TG/DSC, NMR, N2 sorption and chemical analysis). The set of experimental data unambiguously proves successful stabilization of the zeolite framework. Stabilized Ti-containing BEC-type materials were used for methanol photooxidation in order to verify catalytic activity of zeolites obtained by this innovative approach.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...