Natural product inspired antibacterial tetramic acid libraries with dual enzyme inhibition†
Abstract
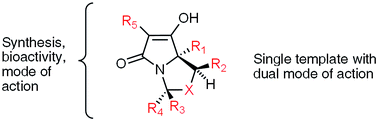
The application of natural product inspired synthesis has identified novel antibacterial tetramic acids which exhibit wide ranging antibacterial activity, and which provide potential lead structures for

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...