Development of a solid phase synthesis strategy for soluble phosphoinositide analogues†
Abstract
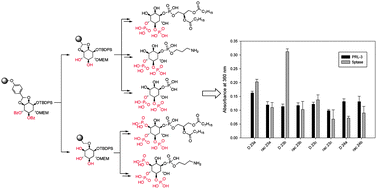
Phosphatidyl inositol phosphates (PIPn) exist in nature with a variety of phosphorylation patterns on the inositol head group. These compounds are vital signaling molecules that regulate numerous key cellular processes. Different enzymes such as kinases and phosphatases modify the phosphorylation patterns. There are only a few structure activity relationship (SAR) studies with PIPn analogues to gather information for the development of PIPn analogue-based inhibitors, because chemical modifications of the inositol head group are very challenging and laborious due to multiple synthetic steps that often require tedious purifications. To simplify such studies, we describe here the development of the first solid phase organic synthesis (SPOS) strategy for PIPn analogues and derivatives providing the basis for the modification of the inositol head group in a combinatorial fashion. Our strategy builds for the first time on only four inositol building blocks to address the seven phosphorylation patterns, and this is enabled by a novel selective benzylidene acetal ring opening on a solid support, which is not possible in solution so far. The first structure–activity-relationship studies using PI(4,5)P2 analogues and derivatives with lipid phosphatases are presented.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...