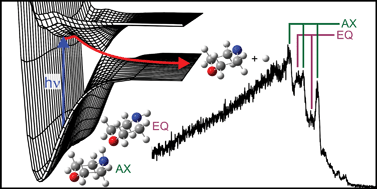
Distinct sets of resolved photoproducts arising from the photodissociation of two neutral molecule conformers have been observed using H(Rydberg) atom photofragment translational spectroscopy methods. This study focuses on the photodissociation of morpholine, at many wavelengths between 250 nm and 193 nm. Morpholine, a six-membered saturated heterocycle with the molecular formula HN(CH2CH2)2O, exists as two ground state chair conformers that are distinguished by the orientation of the N–H bond (axial or equatorial) relative to the chair ring. Complementary MP2, QCISD and DFT calculations all predict the equatorial chair conformer to be lower in energy by ∼250 cm−1. CASPT2(8/8) calculations confirm that both conformers have similar electronic structures, and share a common first excited singlet state, arising as a result of electron promotion from the nitrogen lone pair orbital (n) to the 3s/σ* orbital centred on the N–H bond, forming a 1nσ* state. Photoexcitation to the 1nσ* potential energy surface (PES) leads to N–H bond extension, with the dissociating flux passing through a conical intersection with the ground state PES en route to morpholinyl radicals and H atom photoproducts. Careful analysis of the resulting H atom time-of-flight spectra reveals peaks attributable to the population of specific vibrational states of morpholinyl products arising from dissociation of both conformers, enabling determination of the energy difference between the two ground conformers of morpholine as 180 ± 50 cm−1, and the N–H bond strengths in both the axial and equatorial conformers as 33200 ± 50 cm−1 and 33380 ± 50 cm−1, respectively.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...