Perspectives on plasma-assisted synthesis of N-doped nanoparticles as nanopesticides for pest control in crops
Abstract
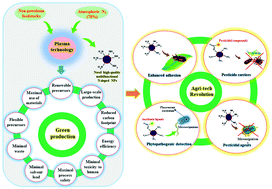
To enhance crop efficiency and meet the growing global demands for food, a new agri-tech revolution has recently been triggering. Engineered nanomaterials have the potential of lessening environmental impact and making agriculture more efficient, resilient, and sustainable. Nitrogen-doped nanoparticles (N-doped NPs) are a rising star toward the development of a new generation of nanopesticides for advanced green agriculture, providing improved efficiency, new concepts for pest control and reduced pesticide resistance, which are key limitations of conventional pesticides. The objectives of this paper are (1) to provide perspectives of promising applications of N-doped NPs as emerging nanopesticides and (2) to review the opportunities which plasma-enabled NP technology is offering for the scalable production of N-doped NPs based on a green, eco-friendly and sustainable approach. The main advantages of the N-doped NPs are their multifunctionality enabling them to provide enhanced adhesion to leaves or insect bodies and several different modes of action to kill insects, including physical, biochemical and catalytic, that are expected to considerably reduce the insect population. Apart from insects, these nanomaterials can inactivate phytopathogenic bacteria and fungi through various mechanisms and are therefore used for a broad spectrum of plant protection. In this review, N-doped ZnO and N-doped TiO2 NPs will be introduced and reviewed as the first examples of these nanomaterials that have been successfully proven as nanopesticides. Following the first demonstration and the application of N-doped carbon dots (N-doped CDs), various agricultural applications such as nanopesticides, pesticide nanocarriers, disease detection, and pest targeting will be reviewed showing their enormous potential to be translated into real applications. The plasma technology comes into play when the focus is on the manufacturing process of these nanomaterials, since, in pest control, producing high-quality nanopesticides is indispensable and challenging. Plasma-chemical NP processing is a green, simple, and rapid approach compared to conventional methods and this review presents how this technology can be used to produce N-doped NPs in a high-quality, high-quantity, low-cost, energy-efficient and sustainable way with minimal waste and without the use of toxic chemicals. The implementation of this technology and introduction of N-doped NPs as new powerful pesticidal agents could make a significant impact on improved crop production.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...