Preparation of a stabilized aqueous polystyrene suspension via phase inversion
Abstract
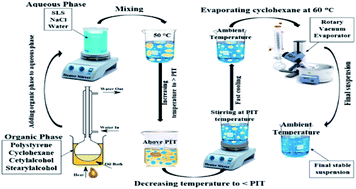
Polymer suspensions have found various applications in novel technologies. In this research, an aqueous suspension of polystyrene was prepared via the phase inversion method using sodium lauryl sulfate (SLS) as an anionic surfactant and two co-surfactants. The effects of co-surfactant ratio and salt concentration were investigated and the stability and characteristics of the prepared samples were identified. All samples possessed a zeta potential lower than −50 mV which reveals an electrostatic stability. The sample PS-1, containing the lower salt concentration of 1 × 10−3 M, was the most stable sample, while its stability decreases with increasing salt concentration. The sample PS-5 during the electrical conductivity measurement exhibited partial instability via agglomeration of polymer on the probe. Rheology measurements revealed that the suspension behavior varies between Newtonian and non-Newtonian. Eventually, PS-1 containing 4.00 g polystyrene, 1.70 g SLS and a co-surfactant ratio of 0.66, suspended within 150 mL of 0.003 M aqueous NaCl solution, exhibited proper stability.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...