The molecular imprinting of magnetic nanoparticles with boric acid affinity for the selective recognition and isolation of glycoproteins†
Abstract
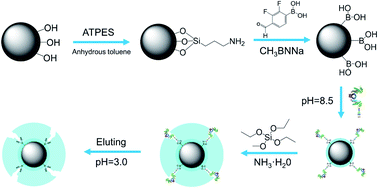
A strategy was designed for the molecular imprinting of magnetic nanoparticles with boric acid affinity (MNPs@MIP) which were then used for the selective recognition and isolation of glycoproteins. Fe3O4 nanoparticles were prepared by a solvothermal method and direct silanization by the condensation polymerization of aminopropyltriethoxysilane (APTES). Subsequently, phenylboric acid was functionalized by reductive amination between 2,3-difluoro-4-formyl phenylboric acid (DFFPBA) and the amido group. The resultant Fe3O4@SiO2–DFFPBA was then used for the selective adsorption of a glycoprotein template. Finally, a molecularly imprinted layer was covered on the surface nanoparticles by the condensation polymerization of tetraethyl orthosilicate (TEOS). The adsorption capacities of the resultant MNPs@MIP–HRP and MNPs@MIP–OVA to horseradish peroxidase (HRP) or ovalbumin (OVA) were significantly higher than non-imprinted particles (MNPs@NIP). Moreover, the adsorption capacities of MNPs@MIP–HRP and MNPs@MIP–OVA on non-template protein and non-glycoprotein bovine serum albumin (BSA) were significantly lower than those of their respective template proteins, thus indicating that both of the prepared MNPs@MIP exhibited excellent selectivity.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...