Bismuthene nanosheets produced by ionic liquid assisted grinding exfoliation and their use for oxygen reduction reaction†
Abstract
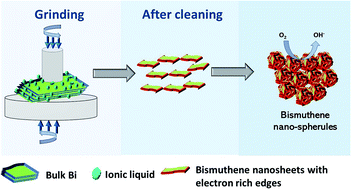
We report the simple synthesis of bismuthene nanosheets (BiNS) by ionic liquid assisted grinding exfoliation, followed by size selection sequential centrifugation steps for the first time. The exfoliation process results in the formation of self-assembled spherule-like superstructures with abundant edge sites, which are able to catalyze the oxygen reduction reaction (ORR) via a two-electron pathway, with a higher efficiency than the bulk Bismuth. We rationalize the enhanced ORR activity of the BiNS to: (i) the presence of 1 dimensional topological edge states, which provide strong conduction channels for electron hopping between the bismuth layers and (ii) the more active role of edge sites in facilitating O2 adsorption and dissociation of O–O bonds compared to the basal plane. The present study provides a pathway for employing 2D topological insulators as a new class of electrocatalysts for clean energy applications.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...