2′-O-Methyl molecular beacon: a promising molecular tool that permits elimination of sticky-end pairing and improvement of detection sensitivity
Abstract
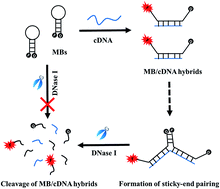
An innovative 2′-O-methyl molecular beacon (MB) has been designed and prepared with improved thermal stability and unique nuclease resistance. The employment of 2′-O-methyl MBs helps efficiently suppress the background signal, while DNase I is responsible for the signal amplification and elimination of sticky-end pairing. The coupled use of 2′-O-methyl MBs and DNase I makes it possible to develop an enzyme-aided strategy for amplified detection of DNA targets in a sensitive and specific fashion. The analysis requires only mix-and-measure steps that can be accomplished within half an hour. The detection sensitivity is theoretically determined as 27.4 pM, which is nearly 200-fold better than that of the classic MB-based assay. This proposed sensing system also shows desired selectivity. All these features are of great importance for the design and application of MBs in biological, chemical, and biomedical fields.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...