Exploring molecular reorientations in amorphous and recrystallized felodipine at the microscopic level†
Abstract
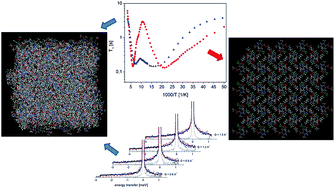
Molecular reorientations were studied in amorphous, partially and fully recrystallized felodipine (calcium channel blocker, a drug from the family of 1′,4-dihydropyridine) using a set of experimental methods: high-resolution solid-state nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR), relaxometry NMR and quasielastic neutron scattering (QENS). The results were compared with molecular dynamics in crystalline felodipine previously investigated [A. Pajzderska, K. Drużbicki, M. A. Gonzalez, J. Jenczyk, J. Mielcarek, J. Wąsicki, Diversity of Methyl Group Dynamics in Felodipine: a DFT Supported NMR and Neutron Scattering Study, CrystEngComm, 2018, 20, 7371–7385]. The kinetics of the recrystallization was also studied. The most stable sample was the sample stored in a closed ampoule (at room temperature, in 0% RH) and its complete recrystallization lasted 105 days. In the fully recrystallized sample, the same molecular reorientation identified in the crystalline form was detected, so reorientations of all methyl groups and the ethyl ester fragment. In the partially recrystallized sample, static disorder caused by the two positions of both side chains was revealed. In the amorphous sample the reorientation of all methyl groups was analyzed and the distribution of correlation times and energy barriers connected with the loss of long-range ordering and disorder of side chains were analyzed. Additionally, inhibition of reorientation in the ethyl ester fragment was observed.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...