A biotin-guided hydrogen sulfide fluorescent probe and its application in living cell imaging†
Abstract
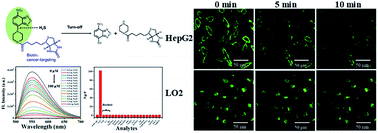
Hydrogen sulfide (H2S), a well-known signaling molecule, exerts significant regulatory effects on the cardiovascular and nervous systems. Therefore, monitoring the metabolism of H2S offers a potential mechanism to detect various diseases. In addition, biotin is significantly used as a targeting group to detect cancer cells exclusively. In this work, a biotin-guided benzoxadizole-based fluorescent probe, NP-biotin, was developed for H2S detection and evaluated in normal liver cell (LO2) and liver cancer cell (HepG2) lines. Results reveal that NP-biotin can detect cellular H2S with high sensitivity and selectivity. Moreover, NP-biotin has been confirmed to possess the ability to target cancer cells under the guidance of the biotin group.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...